SARS-CoV-2 genomics and the growing need for real-time data.
Wisconsin State Laboratory of Hygiene Kelsey Florek, PhD, MPH October 15, 2021
www.k-florek.net/talks

Effects of Mutations
- Synonymous Mutation - A DNA/RNA mutation that does not change the encoded protein sequence.
- Non-Synonymous Mutation - A DNA/RNA mutation that does change the encoded protein sequence, potentially resulting in a change in structure or function.
Comparing non-synonymous mutations to synonymous mutations helps us examine the balance of neutral mutations to beneficial mutations and infer selection.
Positive Selection vs Purifying Selection
- Positive Selection - promotes the spread of beneficial alleles; dN/dS > 1
- Purifying Selection - hinders the spread of deleterious alleles; dN/dS < 1
- Influenza H3N2 HA - example of adaptive viral protein: dN/dS 0.37
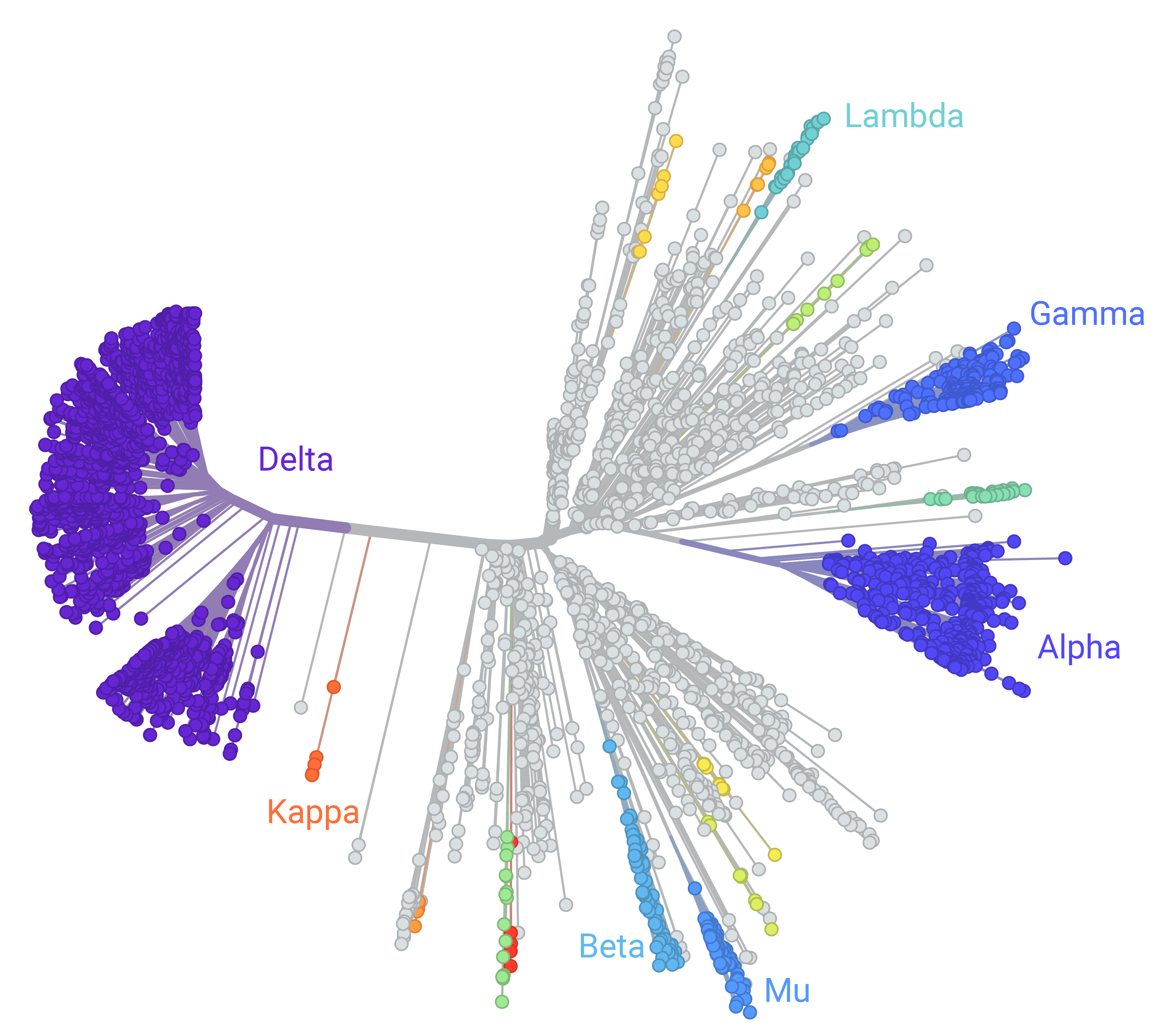
Rapid adaptive mutations in Spike protein
What this could mean
Hypothesis 1: A new selective pressure is acting on SARS-CoV-2 resulting in the appearance of new mutations.
Hypothesis 2: Mutations have altered the spike protein making it more permissive to additional mutations.
"The potential antigenic impact of adaptive S1 mutations, which are accruing at pace over 4 times that of influenza H3N2, suggests that it may become necessary to update the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine strain given the virus’s demonstrated propensity for adaptive change."
The Takeaways
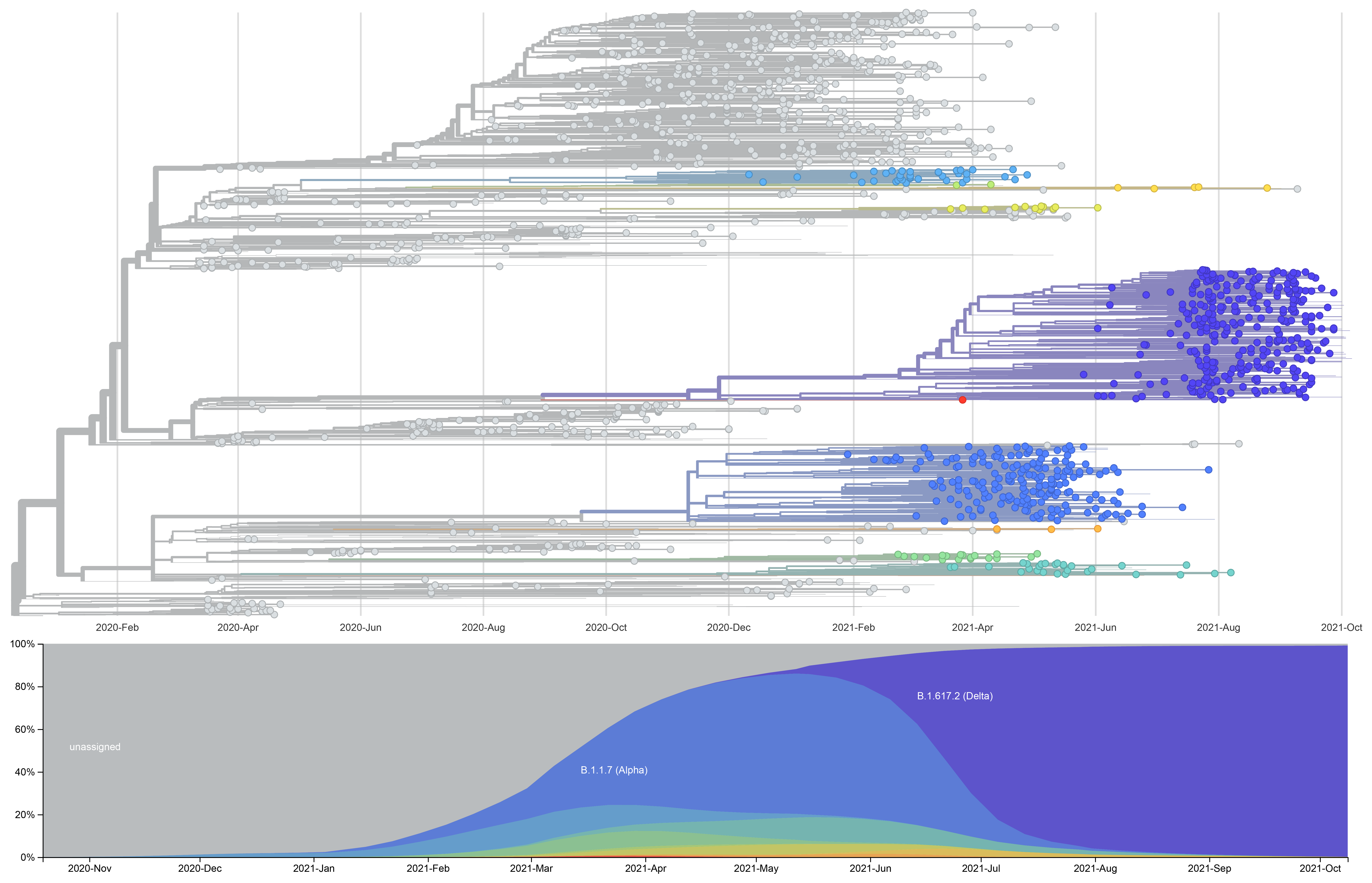
- Likely in the midst of a global Delta selective sweep.
- The Delta lineage may be following a similar pattern to influenza H1N1pdm with a host adaptation phase followed by a sustained antigenic drift.
- Continued genomic surveillance will be needed to monitor for the emergence of mutations that convey vaccine/antiviral breakthroughs, increased transmission, or increased virulence.
SARS-CoV-2 Surveillance Genomics at WSLH
SARS-CoV-2 Sequencing is a collaborative effort
>1,250 members across Federal Agencies, State and Local Public Health Labs, Academic Institutions, Corporations, and Non-Profit Laboratories
SARS-CoV-2 Sequencing is a collaborative effort
SARS-CoV-2 Cases Sequenced
Sequencing Data Generation
Digesting Complex Data for Public Use
- Phylogenetic trees are useless...
- How many have we sequenced?
- Where is the XYZ variant?
- How many sequences are XYZ variant?
- Near real-time summary data!
Dashboard Data Infrastructure
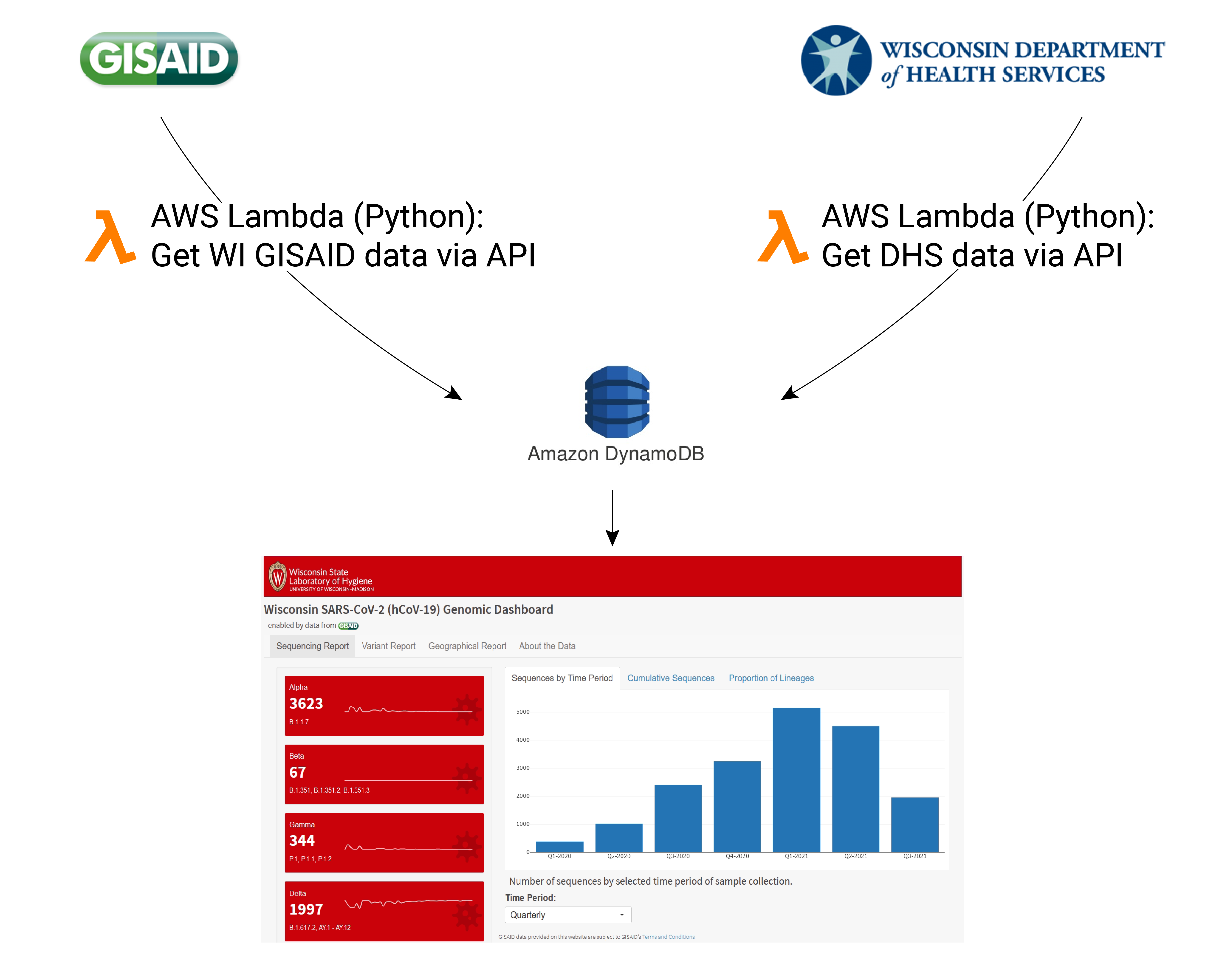
Dashboard Data Infrastructure
- Uses an accessible data analytics language R.
- Somewhat limited in design and implementation.
- Completely automated!
- Dependent entirely on publicly available data served through 3rd parties.
Building a Genomics Data Warehouse
Central repositories of integrated data from one or more disparate sources used for reporting and data analysis.