Applications and use of whole genome sequencing in outbreak investigations.
Kelsey Florek, MPH, PhD November 21, 2019

Slides live from:
www.k-florek.net/talks
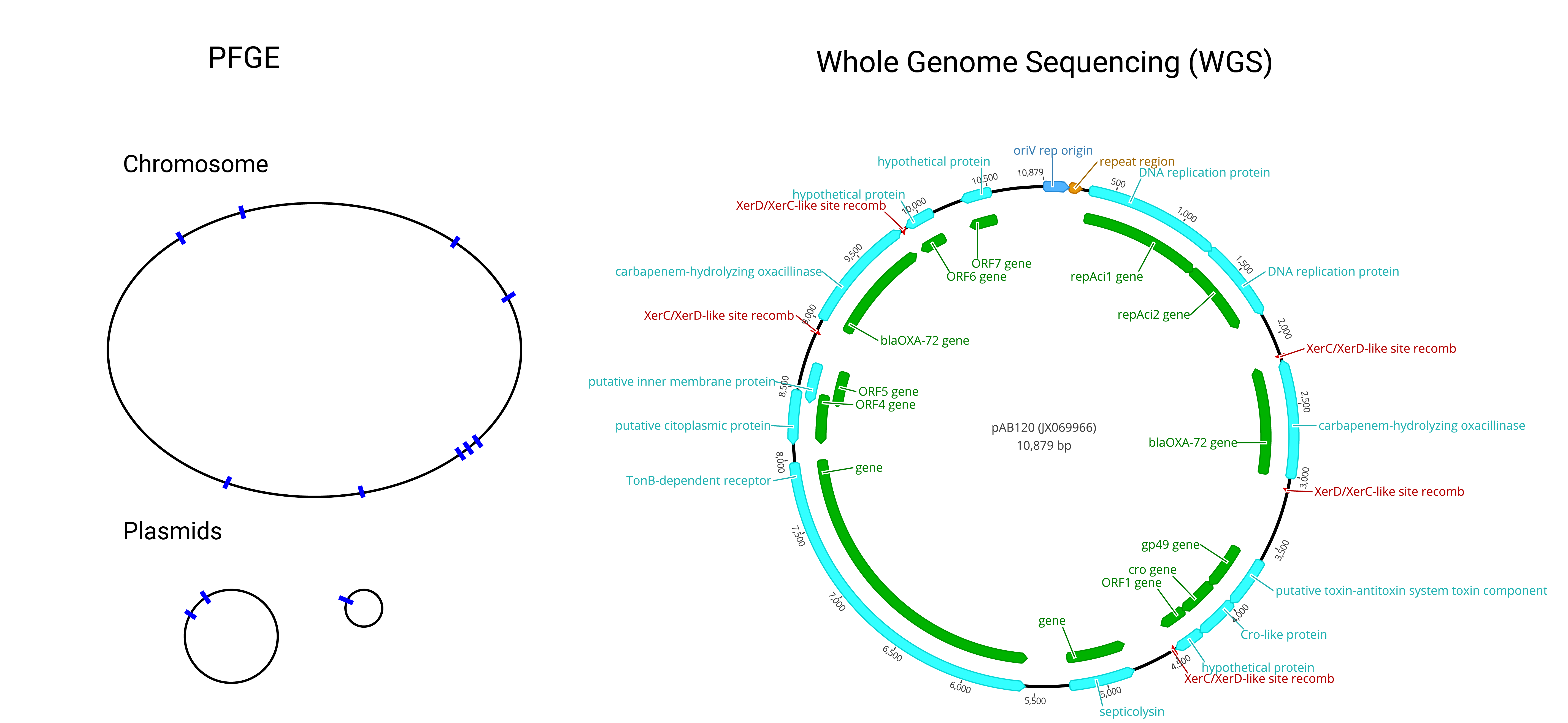
Sequencing has changed how we determine microbial relatedness

Sequencing has changed how we determine microbial relatedness

Sequencing has changed how we determine microbial relatedness

Sequencing has changed how we determine microbial relatedness

Sequencing has changed how we determine microbial relatedness
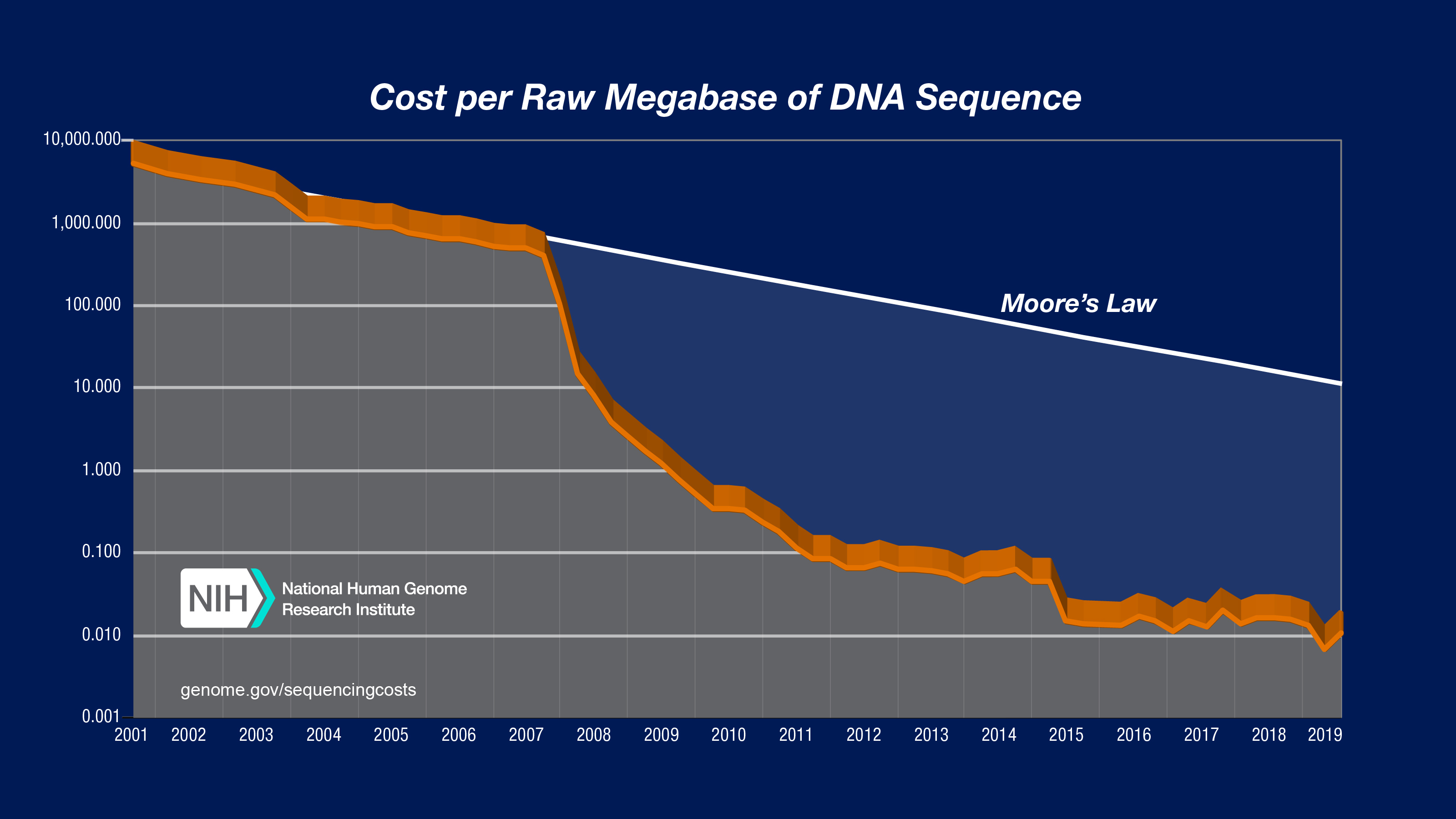
Advances in Sequencing
Sanger Sequencing
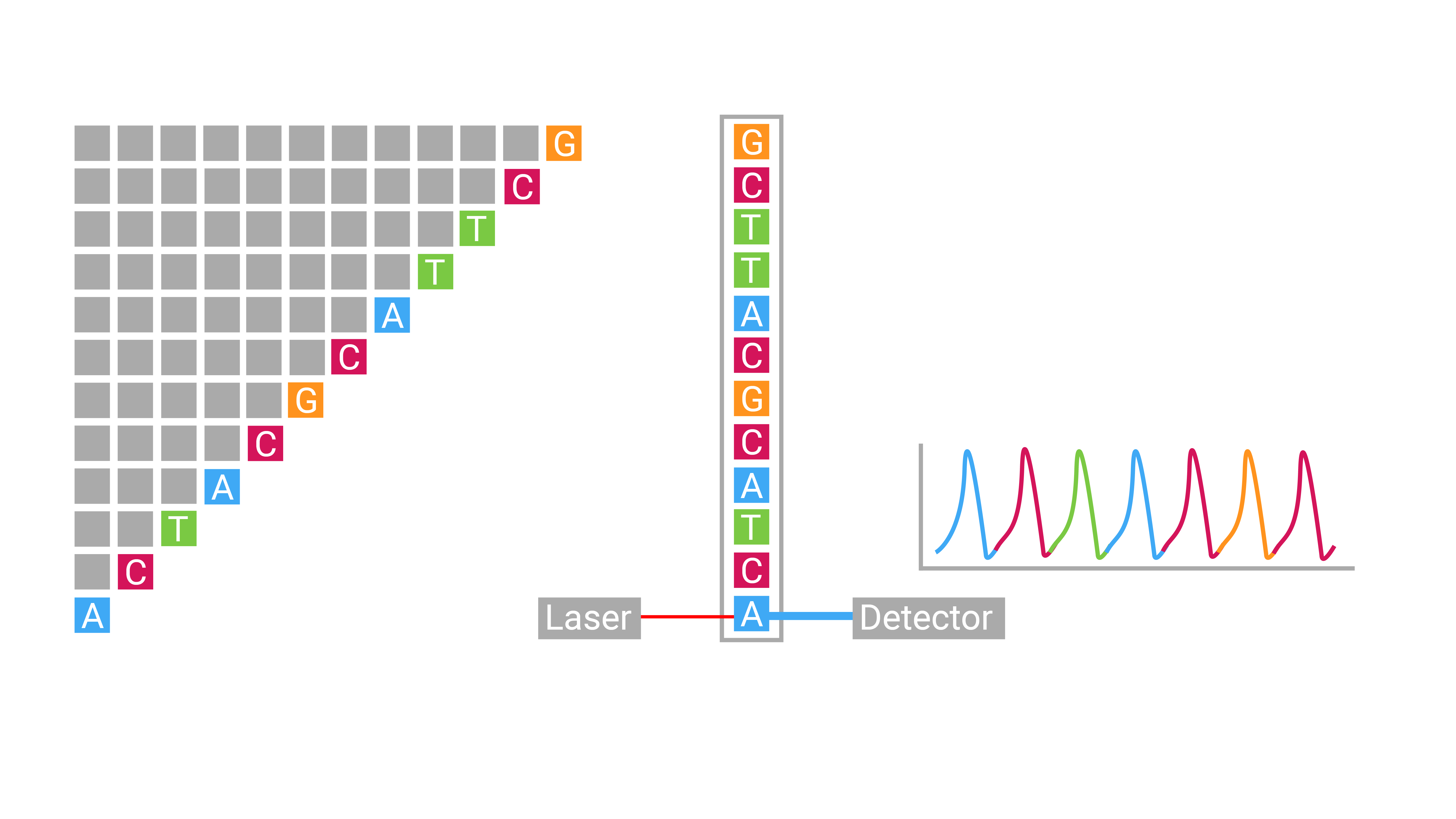
Sanger Sequencing

- max length: 800bp - 1000bp
- throughput: 4 - 32 sequences per run
- cost: $10 per 1000bp
Next-Generation Sequencing
Massively parallel sequencing technology that greatly increases the throughput of genomic sequencing.
Illumina Sequencing
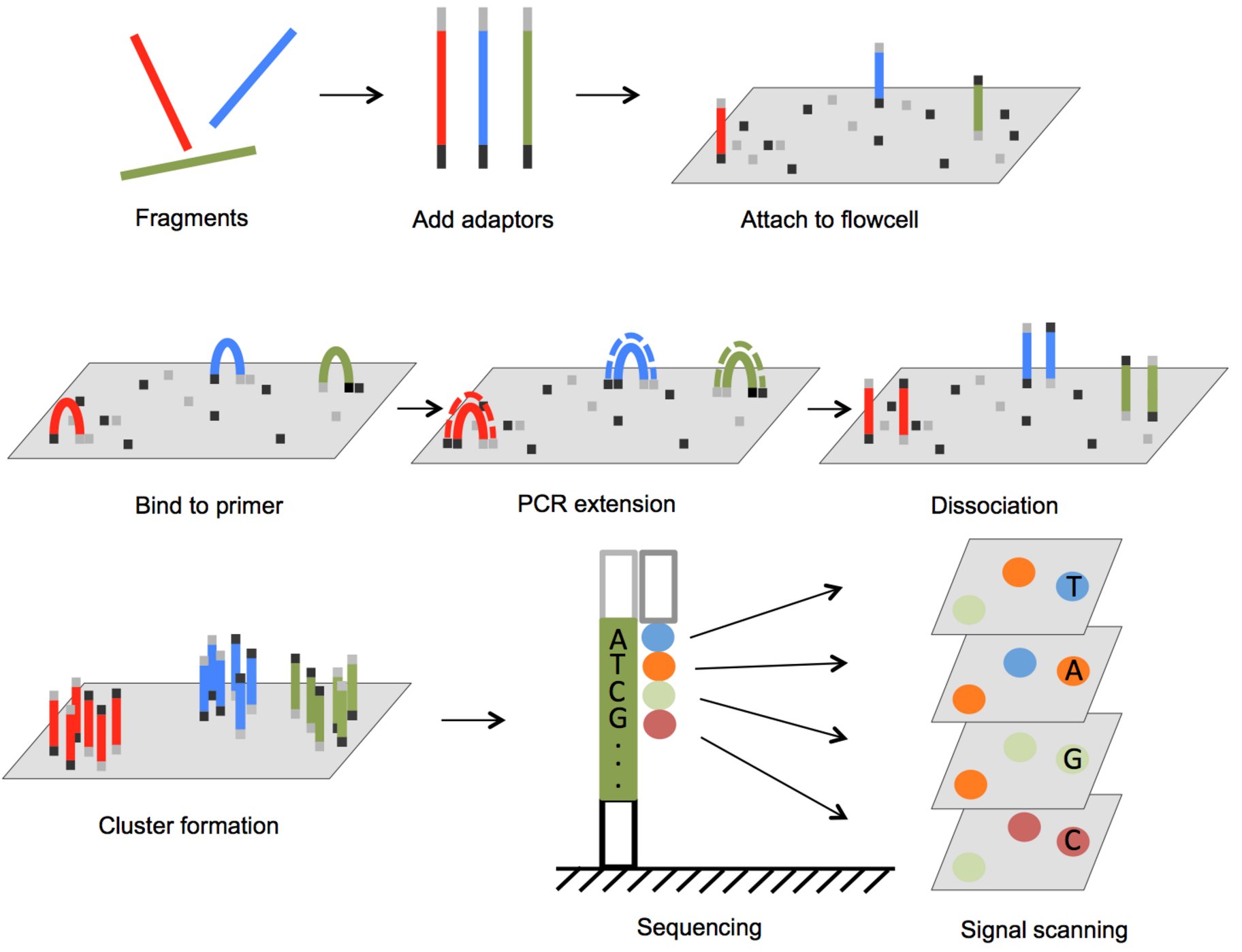
Illumina Sequencing

- max length: 2 x 300bp
- throughput: 25 million sequences per run
- cost: $0.0005 per 1000bp
Increases in data requires advanced analyses
- 15 Giga Bases generated per MiSeq run
- 40,000 - 150,000 words in a novel
- average word length in English is 4.79
- one sequencing run would generate 3,296 novels with 95,000 words each
Bioinformatics
What is Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS)?
How is it used and what can we gain from using it?
Shotgun sequencing approach
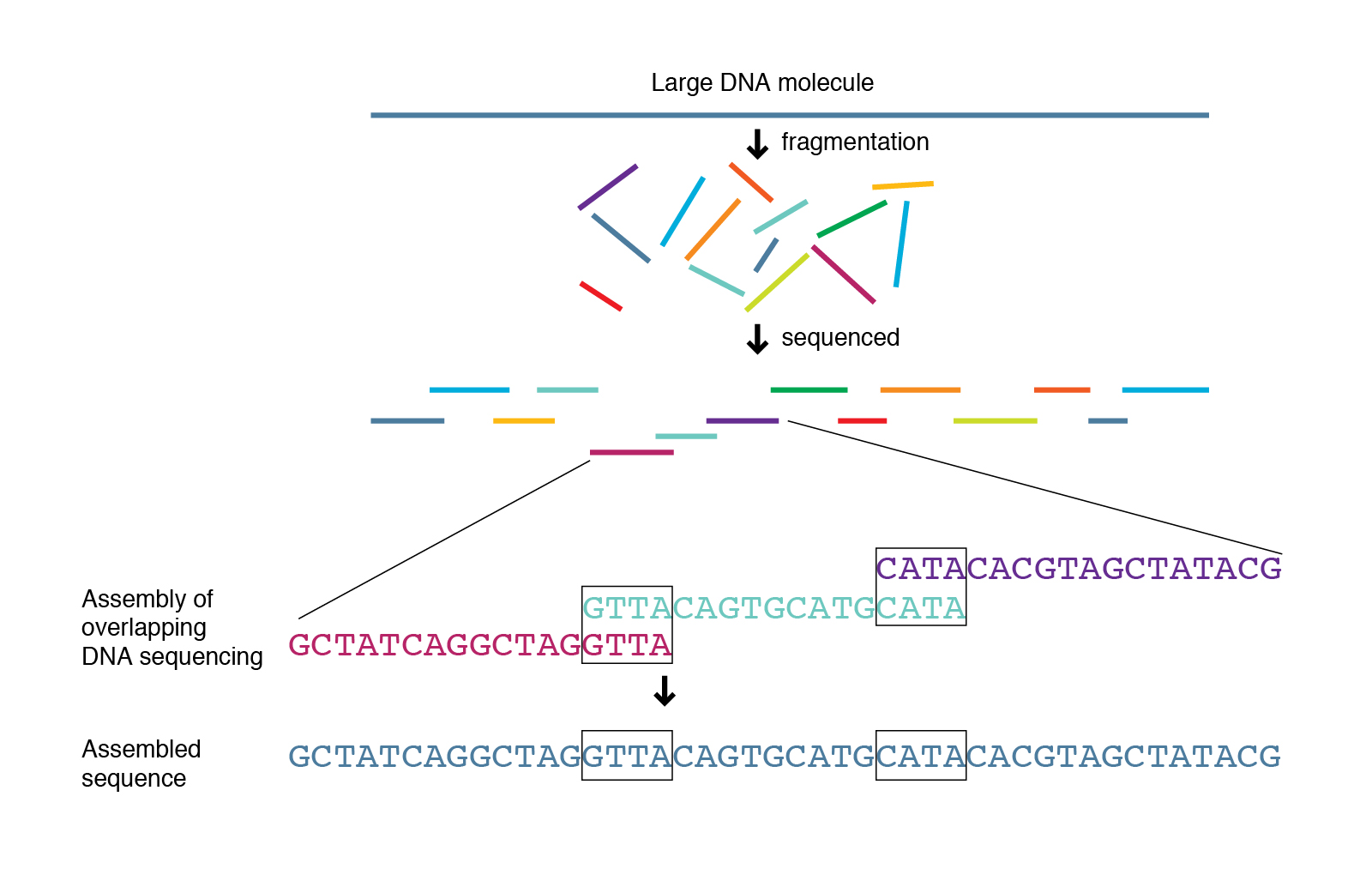
Shotgun sequencing approach
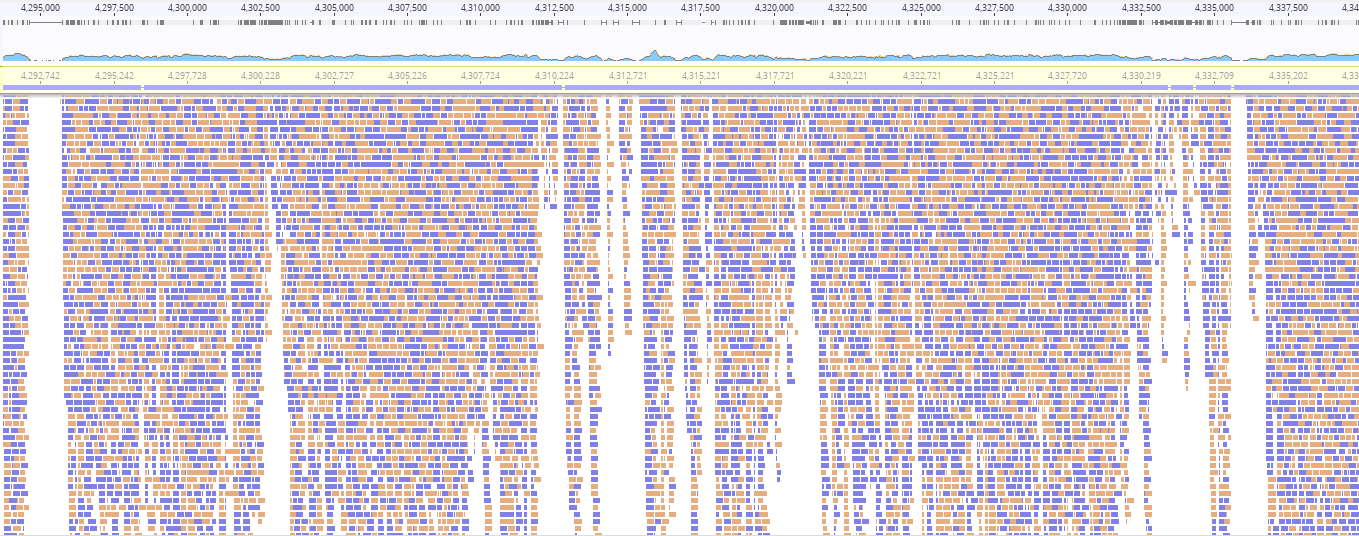
To infer bacterial relationships from sequence data we have to consider the effects of evolution.
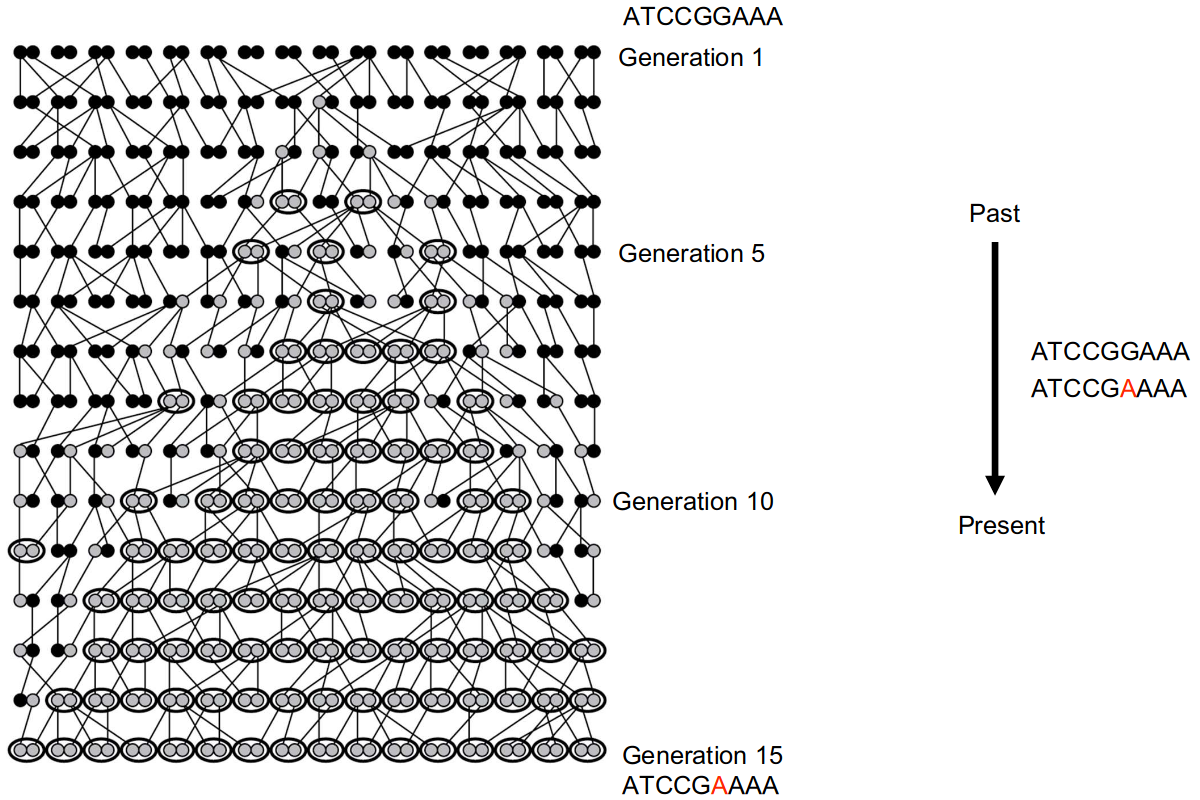
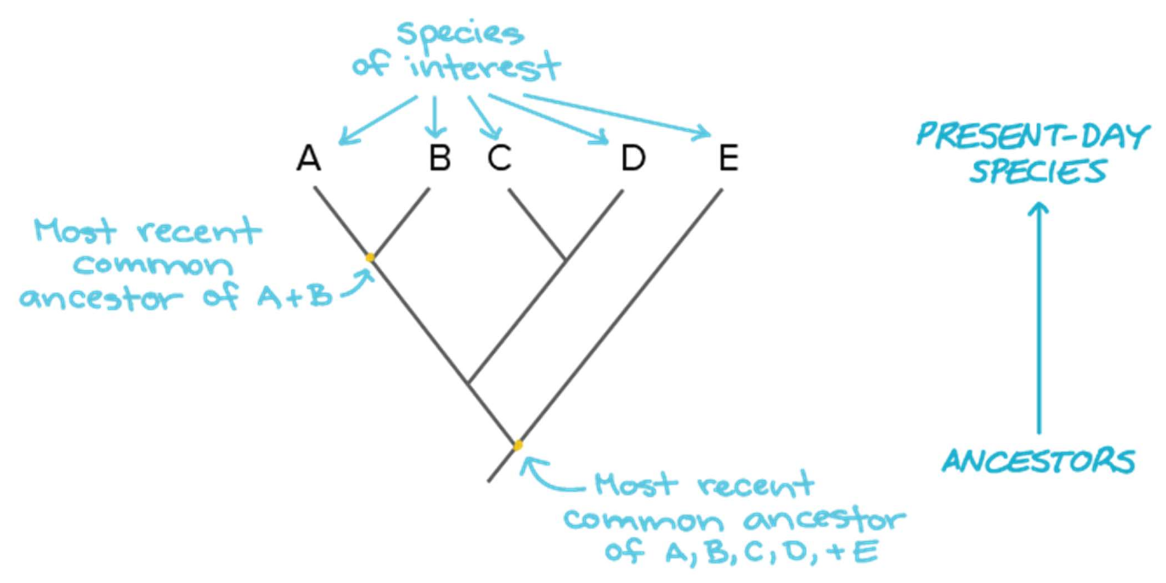
There are several approaches to measure the relatedness of isolates
- Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms or SNPs
- MLST
- wgMLST
- Core-genome Relatedness
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms
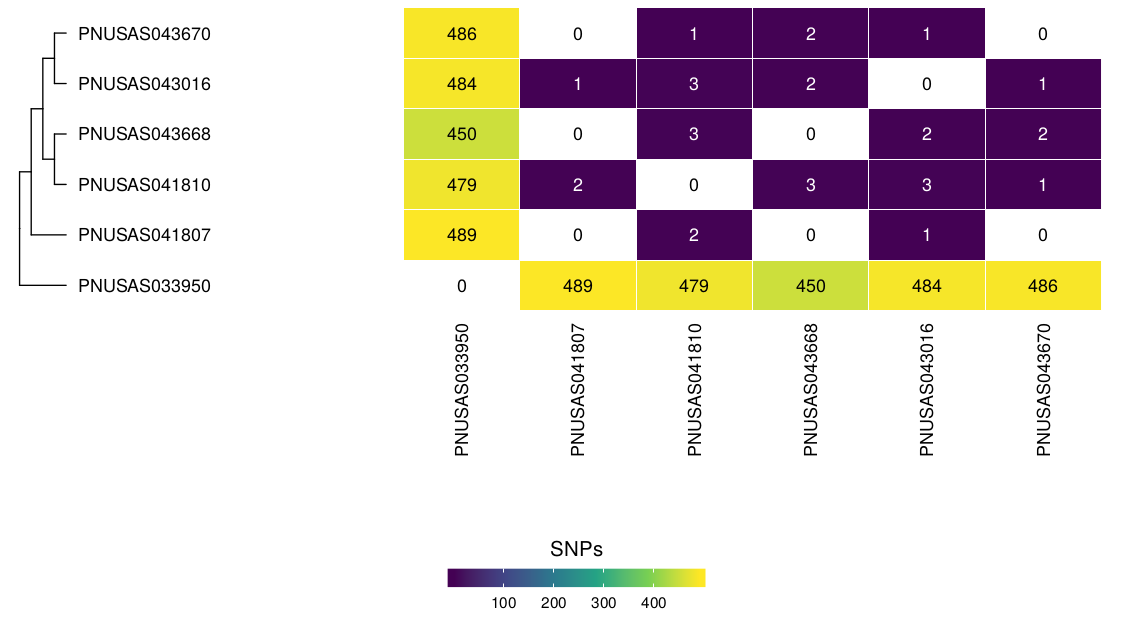
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms
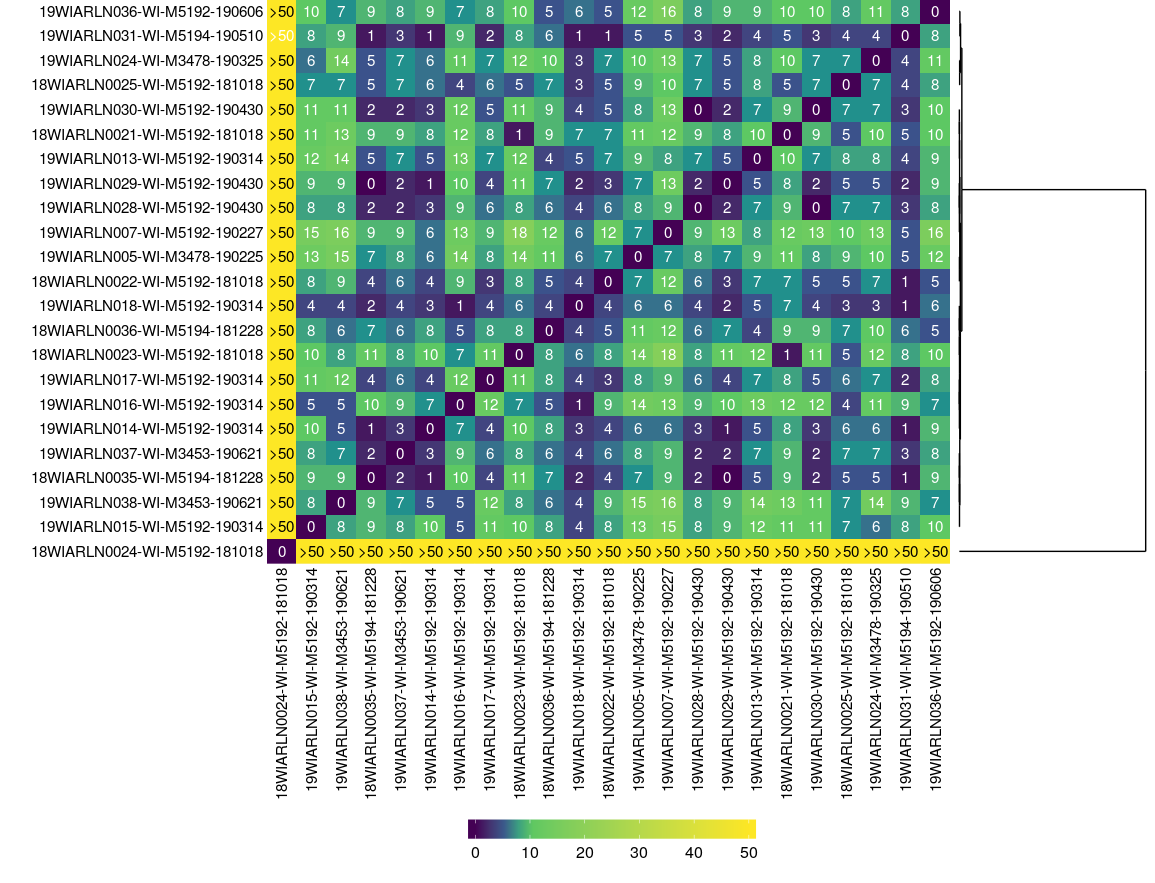
Multi-locus Sequence Typing or MLST
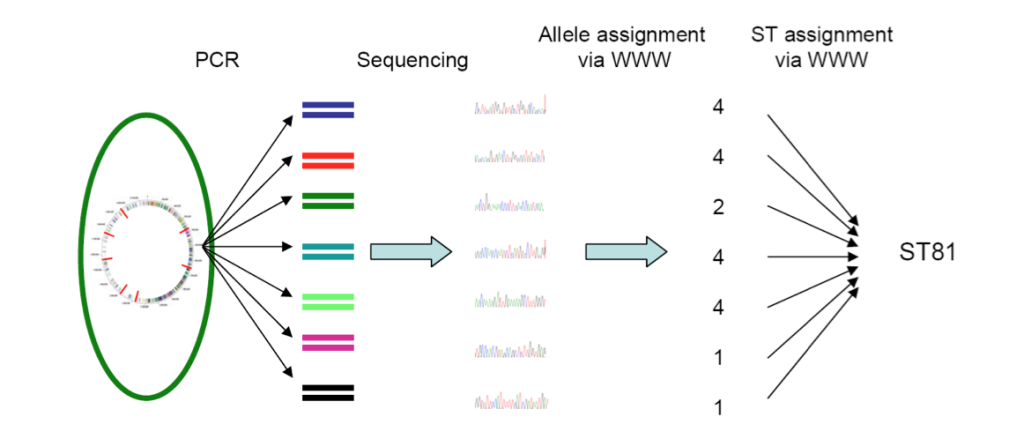
whole genome MLST or wgMLST
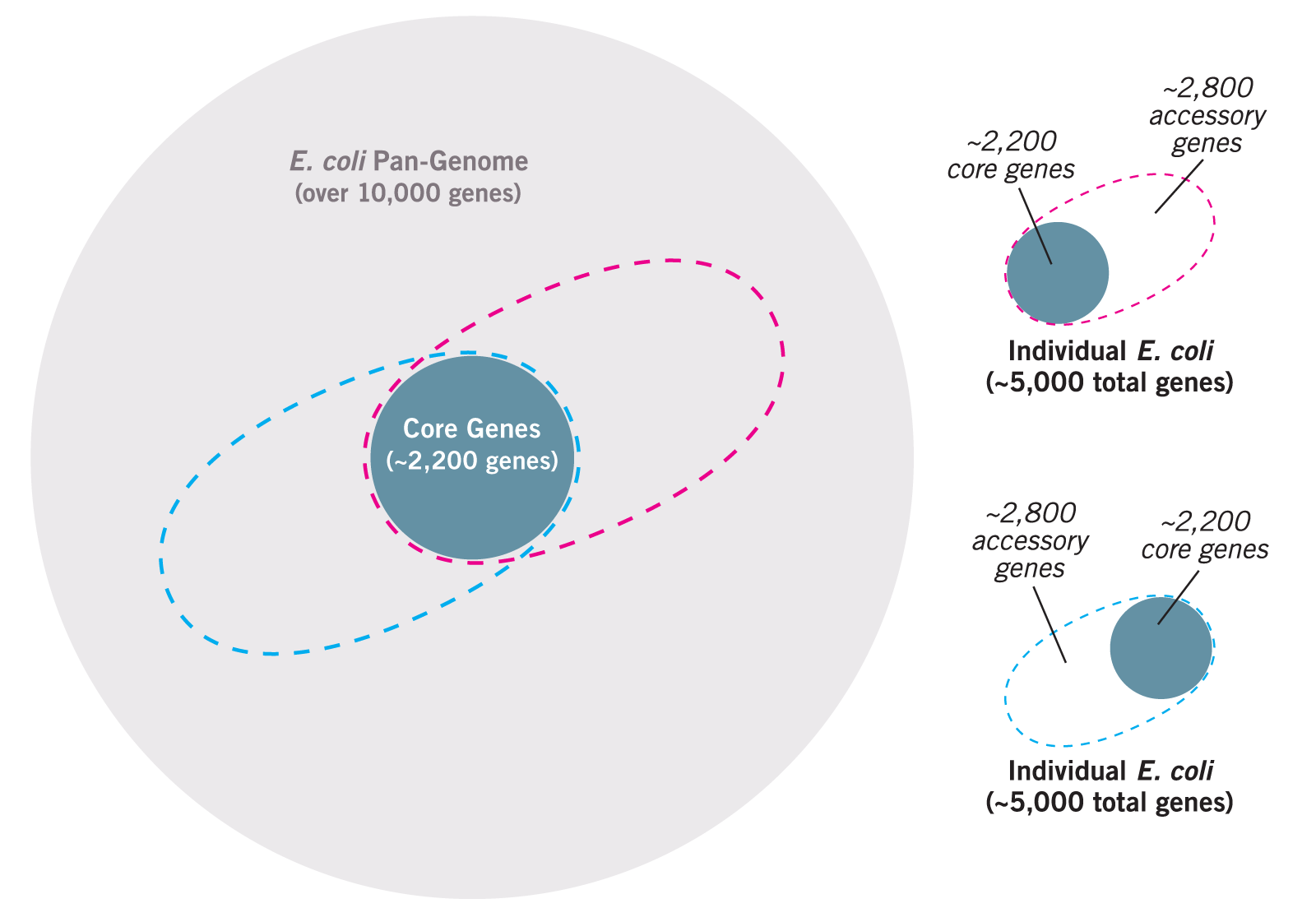
whole genome MLST or wgMLST
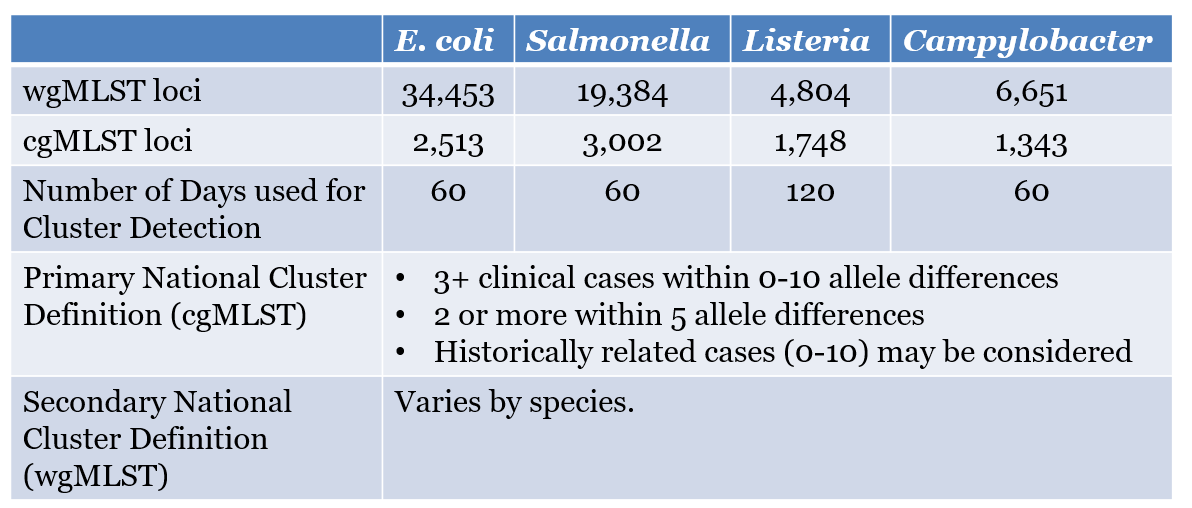
core-genome comparisons
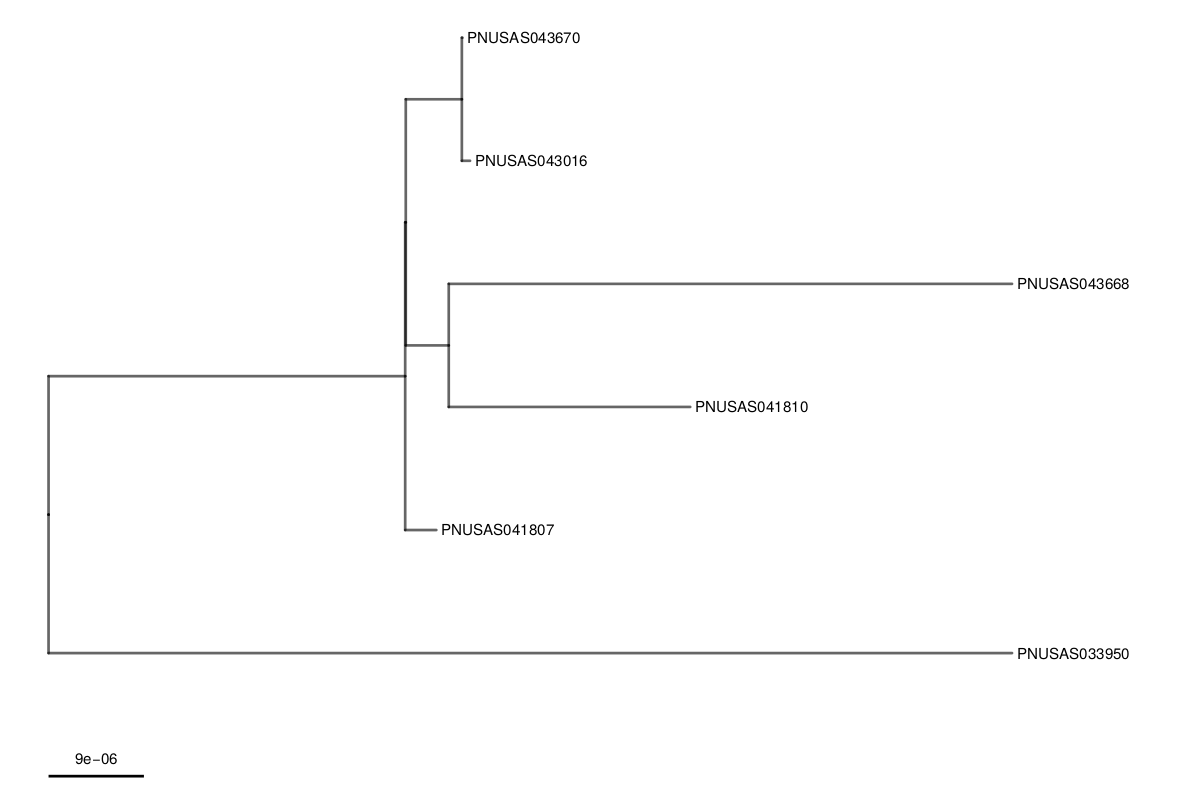
Moving beyond WGS
